News & Resources
Explore our News & Resources

Forensic Investigations
Deflection of in-span hinges in prestressed concrete box girder bridges during construction
Multi-span cast-in-place (CIP) post-tensioned concrete (PS) box girder bridges undergo upward deflection (curl) at hinges due to post-tensioning forces. Adjustments in falsework height are often necessary in the field to address the curl and avoid bumps, which cause traffic safety concerns and present a road hazard. A current method to estimate hinge curl has often led to results that are significantly different than those measured in the field thus causing construction delays and costly change orders.

Forensic Investigations
Wall-Like Reinforced Concrete Columns Externally Confined by means of Glass FRP Laminates
This paper discusses the laboratory testing of wall-like reinforced concrete (RC) columns externally confined with glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP) laminates and subjected to pure axial load. Specimens were characterized by an overall length of 3.05 m (10 ft), cross-sectional dimensions of 356 by 1,041 mm (14 by 41 in). Three specimens were tested: one was unstrengthened (benchmark) and two were confined with GFRP laminates. Two different confining reinforcement ratios were considered.

Forensic Investigations
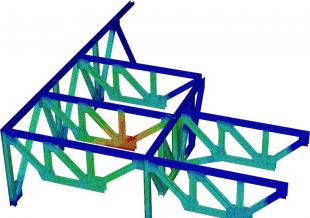
Time-Dependent Analysis of Post-Tensioned Bridge Hinge Curl
Accurate prediction of instantaneous and time-dependent deformation of superstructure in-span hinges is important for preventing a mismatch of bridge decks. Time-dependent deflection of in-span hinges hinge curl in posttensioned bridges depends on the construction sequence and the material time-dependent properties. Structural analysis software is an important tool for estimating time-dependent deformations. Computational modeling was conducted to calculate the hinge curl in posttensioned bridges considering two approaches, the spine model and the three-dimensional finite-element model.
Forensic Investigations
Sensitivity Analysis on Design Parameters
Performance based fire engineering has recently been the focus of several studies due to its well-known benefits and the short-comings of the traditional prescriptive design methods. However, the method is not often used extensively because of the large number of parameters and decisions involved in the process. This study presents a framework to conduct a number of sensitivity analyses to help the engineer determine which of several parameters used in a performance based design can affect the outcome significantly.

Forensic Investigations
Weighty Matters: An Overview of In-Situ Load Testing
In-situ load testing is a powerful tool to assess the performance of structures with respect to their ability to carry code-prescribed loads. The practice dates back to the late 1800s and has been used to verify the load rating of structures, as well as the expected performance of structures in retrofit, repair, and strengthening applications.
 Jocelyn Kinghorn/Flickr
Jocelyn Kinghorn/Flickr
Forensic Investigations
Resistance and Failure Behavior of Ductile Concrete-Filled Double-Skin Tube Columns
Fire following an earthquake has been a major cause of damage in a number of historic seismic events. Considering the amount of damage and statistics showing a high probability for the occurrence of post-earthquake ignitions, there is a need to study the effects of seismic damage on the fire resistance of structures. This research studies the resistance and failure behavior of Concrete Filled Double-Skin Tube (CFDST) columns with both experimental and numerical methods.
 Courtesy Wikimedia
Courtesy Wikimedia
Forensic Investigations
Investigation of Sprayed Fire-Resistive Material and In Situ Bond Failure
This paper reviews several case studies of spray fire-resistive materials (SFRMs) and provides lessons learned over the course of the forensic investigations. ASTM E736-00 Standard Test Method for Cohesion/Adhesion of Sprayed Fire-Resistive Materials Applied to Structural Members (ASTM 2006) is used to determine the bond strength of newly cured SFRM. The International Building Code (IBC) 2015 (ICC 2014) specifies minimum acceptable bond strengths. The validity of those bond strengths as applied to in-service SFRM is considered.

Forensic Investigations
Investigation of Fragment Impact and Blast Shock Wave on Window Breakage
A natural gas explosion in East Harlem, NY destroyed two buildings and caused breakage of windows on a building across the street from the explosion. The equivalent TNT charge of the explosion is estimated and used to develop an explosion-fragment model (EFM) of the explosion event. The EFM is employed to investigate the potentiality of the window breakage as being caused by fragment impact or by the blast shock wave itself.
